SEO, the acronym for Search Engine Optimization, in simple terms is the process of increasing your website’s visibility on a search engines. With the goal of gaining more free traffic, SEO is all about satisfying your audience’s search intent.
The higher your web pages rank, higher will be the number of visitors. Good SEO practice attracts more visitors who might become your customers or regular reader.
Here, in this blog, we will cover everything that you need about know SEO marketing with a free template to help you plan your strategy for 2023.
So read on to learn SEO the right way!
Click here to download the customized ‘ SEO Strategy Template ‘
Understanding Search Engines.
Search engines are like digital libraries. And Instead of copies of books, these hold copies of websites. So when you enter any search query, it searches through all of the pages in its index and returns the most relevant results with the help of an algorithm.
Although, it’s difficult to understand the algorithm of a search engines, but what we do know that:
‘Search algorithms consider numerous aspects, including the words in your query, the relevancy and usability of pages, the expertise of sources, and your location and settings, to provide you with the most beneficial information. The importance of each aspect changes depending on the nature of your inquiry; for example, the freshness of the content is more important when answering questions about current events than it is while answering questions about dictionary definitions.’
When it comes to Google, it is the search engine that most of us use—at least for web searches. This is due to the fact that it has by far the most reliable algorithm.
However, there are numerous more search engines for which you can optimize your website.
What is SEO?
As mentioned earlier, SEO shows search engines that your material is the best result for the topic at hand. All search engines aim to provide users with the best, most relevant results. However, your exact method depends on the search engine you’re optimizing for.
Taking Google as the default search engine, let’s see how SEO works. To increase organic traffic to your website from Google, you must first understand and cater to Google’s algorithm.
Note: Organic traffic refers to the not-paid traffic that your website gains by ranking on search engines. In other words, people find your website “organically” because it matches what they’re looking for, rather than through paid advertising.
SEO takes place ‘on-site’ and ‘off-site’ which practically involves:
A. Keyword research.
B. Creating & optimizing content.
C. Technical Optimization.
D. Link Building Strategy.
Importance of SEO.
3.8 million people hit the search button on Google every minute. So, 228 million people search on Google every hour, which makes near about 5.6 billion searches per day and 2 trillion searches per year.
The numbers are no doubt staggering. And it is no surprise that search engines like Google are the biggest source of website traffic.
So how do you harness this potential of the search engine? And the answer is by appearing on search results. Let us work out the correlation here- the higher you rank on search results, the more traffic you will receive.
A study by Backlinko suggests that the No.1 organic result usually gets 10X more clicks than a page ranking on No. 10. The top 3 suggestions on the search results receive more than 50% of the clicks.
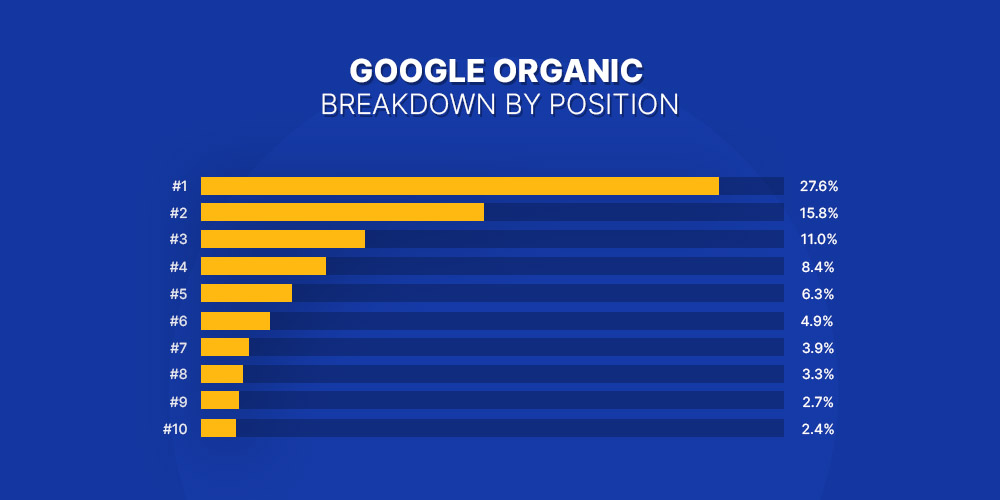
And this is where SEO comes into play.
SEO plays a strategic role in your ranking factors set by Google. A higher ranking means more traffic, which in turn converts into more customers and increases brand awareness.
Not focusing on SEO would leave a lot of space for competitors to fill in and gain traffic to generate revenue.
Want to how to improve your WordPress site’s SEO? Read here.
SEO or PPC?
Whenever you search on Google, you will find two kinds of results:
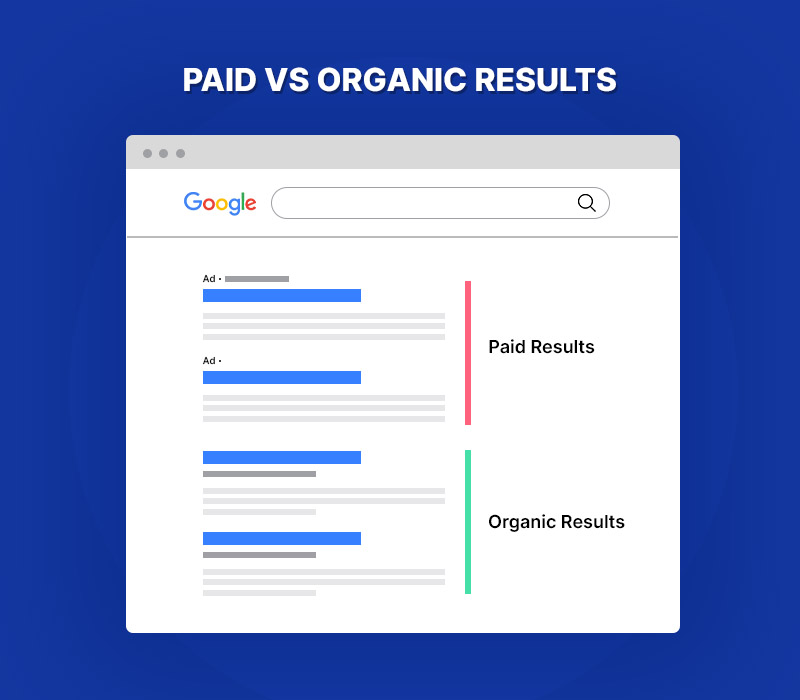
A. Paid Results- The results with ‘Ads’ in front of them are the results from pay-per-click advertising. As the name suggests, you will have to pay to be there.
B. Organic Results- The results after the ads are the organic results.
Now a question arises. Why not pay to be on the top?
The answer lies in the research by First Page Sage, which suggests that visitors often ignore the ads and instead click on the organic results.
Here is a pie chart to paint a better picture for you.
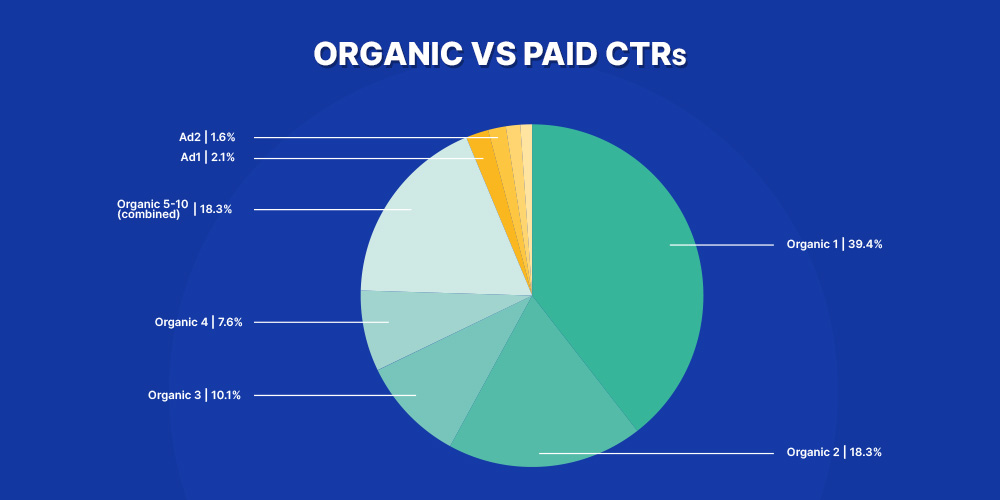
SEO demands more effort, yes. But it focuses on ‘free’ organic traffic. And once you are on 1st, this traffic will not disappear.
Types of SEO.
There are 4 types of SEO working simultaneously:
a. On-Page SEO.
b. Off-Page SEO.
c. Technical SEO.
d. Local SEO.
Deploying your resources with a particular skill set on each is important. Let’s understand each of the above in detail.
On-page SEO.
On-page SEO focuses on the content present on your website. To rank well on search engines and attract visitors, your website must feature easily discoverable and comprehensible content. Additionally, Google emphasizes a preference for content that provides valuable assistance.
The optimization of the content & webpages comes under the On-page SEO, with:
a. Keywords.
b. Writing content.
c. URLs.
d. Headers.
e. Title Tags.
f. Images.
The on-page or ‘on-site’ SEO factors can be carried directly on pages. Here are a few tips and practices to help understand these factors better:
A. Keywords:
1. Performing keyword research: Before you go ahead and write your article, carry your keyword research with a tool such as Semrush. You can easily see the phrases people are looking for, how certain they are searching for, etc.
2. Using keywords strategically: Consider inserting target keywords in areas like the header, first paragraph, and title tag to tell readers and Google what topics are important.
3. Don’t stuff: While it is crucial to incorporate your target keywords, avoid repeating them to improve your rankings. This is a spammy strategy that Google does not support. It’s also unappealing to readers.
B. Writing Content:
1. User Experience: Make sure your written information is easy to understand. Use brief paragraphs, bullet lists, charts, and other visual aids.
2. Focus on answering the questions: Keep in mind that most visitors to your page are looking for an answer to a question. If you’re writing about “Mercedes-Benz SUV pricing,” those figures should be prominently displayed at the top of the page.
3. Competitor Research: Take a look at what pages currently appear when you search for your desired term before making a post. What can you do better?
C. URLs:
1. Use KWs in URLs: The URLs should be easy to recognize by the search engines and the readers.
2. Separate words using hyphens: URLs do not contain spaces, and Google prefers hyphens to underscores to separate words.
3. Say no to Stop Words: Stop words (the, and, or, of, a… and so on) can lead to jumbled URLs that are difficult to read. To keep your URL understandable, avoid using stop words. This also helps keep URLs brief.
D. Headers:
1. Use headers: For a better user experience, headers can assist in segregating material. They can also assist Google in determining how a page is structured.
2. H2, H3, H4….. and so on: Sub-headers can help to break up large pages and improve the user experience. Use H2 headings for key sections, H3 for supporting points, and H4 for minor points.
3. KWs in headers: As previously said, this can assist visitors and search engines in determining what the website is about.
E. Title Tags:
1. Keep it short & simple: Google will chop off your title tag after 70 characters. 50-60 characters is a decent rule of thumb to incorporate enough important information without cutting off the title tag.
2. Stand by your words: Nothing is more frustrating for a user than clicking a link to a page and discovering that the content does not provide what the title tag and meta description promised.
3. Include KW at least once: While it’s generally a good idea to include your primary keyword—because that’s what the page should be able to do—avoid cramming in a bunch of keywords just because there’s space.
E. Images:
1. Picture says a thousand words: Many users will not bother to read a wall of text. Include visuals and screenshots frequently, especially when instructing a user on how to do something.
2. Use ‘alt text’: The alt text of a picture tells Google what the image depicts. Visually impaired people can also hear image descriptions.
3. Compress Image: Using huge image files can cause your page to load slowly and provide a poor user experience. Image compression programs such as TinyPNG and ImageOptim are accessible for free.
Off-page SEO:
Off-page SEO refers to activities made outside of your website that can help you rank higher, such as:
A. Link Building.
B. Social Media Marketing.
C. Guest Blogging.
D. Customer Testimonies.
Site owners, unlike on-page SEO, do not often have a direct influence on these initiatives.
A robust off-page SEO strategy and a positive internet reputation demonstrate to search engines that your site is trustworthy and credible.
A. Link Building:
1. Quality over Quantity: Get backlinks from high-quality & authoritative websites of your niche.
2. Don’t buy: Since Google is smart enough to recognize the spam technique, buying links can harm the performance of your websites.
3. Infographics are amazing: It has been found that infographics engage 30 times more than regular content, so try to include more of these.
B. Social Media Marketing:
1. Be proactive: You may gradually grow your brand reputation by frequently publishing, responding to comments, and reporting on newsworthy updates in your niche.
2. Include several platforms: If you exclude social media sites from your overall plan, you may miss out on many potential clients. For example, your LinkedIn audience will most likely be extremely different from your Instagram audience.
3. Content repurposing: Once you’ve created a blog article, you’ll have many possibilities for repurposing it across many platforms, including social media sites. Share an informative piece on LinkedIn, make a poll on Twitter, make a related Instagram meme, and so on.
C. Guest Blogging on other websites :
1. Collaborate but be careful: Don’t guest post for any site that offers it. If you’re only participating for the links, you’re phoning it in. Choose a collaborator and work together to generate useful content that fills a void in your specialty.
2. Authenticity: When feasible, use original data and research. Collaboration on a study is a terrific approach to giving something unique to your community through guest posts.
3. Content first: Backlinks are beneficial, but the primary goal should be to develop outstanding content. If you continually link back to your site, the content may lose credibility and appear spammy in Google’s views.
D. Customer Testimonies:
1. Google Business Profile: From your Google Business Profile, you may respond to Google reviews, answer questions about your business, set your hours online, and more (GBP). We’ll go over local SEO in greater detail later.
2. Communication is the key: Both the good and the bad! This contributes to the development of trust between your brand and its customers. Or even prospective clients.
3. Don’t be generic: Rather simply responding with “thank you for your review,” take the time to personalize your responses. This is especially critical when a customer has a complaint or a problem with your company.
Technical SEO .
Consider your website to be a theatre. The technical SEO components would be the backstage job.
The show would not be possible without these behind-the-scenes efforts.
To ensure your site’s technical health, conduct an SEO audit regularly. You can use a program like Site Audit to determine whether you have any faults or errors that need to be addressed.
This will include:
A. Sitemap.
B. Website Architecture.
C. HTML, CSS & JavaScript.
D. Crawlability.
E. Schema.
F. Page Speed.
Local SEO.
Local SEO is the technique of increasing your local search visibility. A local business listing provider may assist you in locating and optimizing for local keywords, as well as optimizing your Google Business Profile and establishing local citations.
This could include a combination of on-page and off-page SEO methods, as well as improvements for external directories and maps.
This section will concentrate on two major pillars:
Google Business Profile.
Local Citation.
How to Optimize for Google:
Google generally employs over 200 ranking variables.
Even back in 2010, there was speculation that there could be up to 10,000. Nobody knows the full list of ranking determinants, but we do know a few of them.
How? Face the reality that there is an increase in the number of persons in the rankings and the fact that there is an increase in the rankings.
We’ll go through some of them shortly. But first, a very important point to consider:
Google doesn’t rank websites, it ranks web pages.
Because your company manufactures stained glass windows, it does not follow that every page on your website should rank for the query “stained glass windows.”
With different pages, you can rank for different keywords and themes.
Now, let’s look at some of the factors that influence rankings and search engine visibility.
Crawlability:
Before Google can even consider ranking your material, it must first be aware of its existence.
Crawling is the primary strategy used by Google to discover new content on the web. To put it simply, crawling is the process by which Google follows links from pages it already knows about to pages it hasn’t seen before.
They utilize computer software known as a spider to accomplish this.
Assume your homepage contains a backlink from a website that is already indexed by Google.
When they crawl that site again, they’ll follow that link to find your website’s homepage and most likely add it to their index.
They’ll then crawl your homepage’s links to find other pages on your site.
With that being said, here are a few things that should be taken care of:
A. Internal Links & No-follow: Google uses internal links to crawl all of your site’s pages. Pages that lack internal links are less likely to be indexed. Google will not crawl internal links with no follow tags.
B. Page not indexed: A no-index meta tag or HTTP header can be used to exclude pages from Google’s index. If other pages on your site simply have internal connections to no-indexed sites, Google may not find them.
C. Robots.txt: A robots.txt file tells Google where it can and cannot go on your website. It will not crawl pages that are prohibited here.
Mobile Responsiveness:
Mobile devices account for 63% of Google searches, and this figure is increasing year after year.
Given that figure, it’s no surprise that Google revealed a ranking increase for mobile-friendly websites in its mobile search results in 2016.
In 2018, Google also implemented mobile-first indexing, which means that the mobile version of your page is now used for indexing and ranking.
In other words, when a desktop version of a site loads on mobile, most visitors will hit the return button.
This is significant because Google wants to keep its users happy. Pages that aren’t mobile-friendly cause unhappiness. Even if you do rank and earn the click, the majority of people will not stay to read your content.
Page Speed:
Page speed refers to how quickly your page loads. It is a desktop and mobile ranking factor.
Why? Google wants to keep its users happy once more. If their users click on search results that take too long to load, they will be dissatisfied.
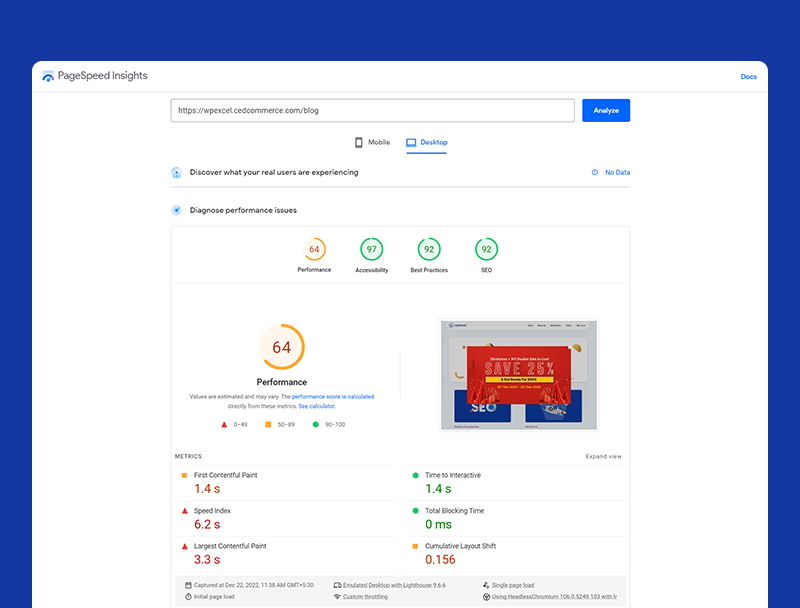
Use Google’s Pagespeed Insights tool to test the speed of your web pages.
Search Intent:
Often, marketers overlook whether their page corresponds to the search purpose of their chosen term. Google interprets the query’s intent and displays the user’s desired results.
To satisfy the search intent, consider the 3 C’s in the search results of Google:
A. Content-Type: Are the majority of the results blog articles, product pages, category pages, landing sites, or some other type of page?
B. Content Format: Is Google primarily ranking how-to guides, list-style articles, tutorials, comparisons, opinion pieces, or something else? (Note. This one mostly applies to informational themes.)
C. Content Angle: Is there a recurring theme or distinct selling feature among the top-ranking pages? If this is the case, you now have some idea of what searchers are looking for.
So this is what SEO is in practice. But there are a few truths you should must know before you set on your SEO journey:
SEO is not about:
A. Cheating Google: Rather than cheating the search engines, think of SEO as convincing the engine to rank higher by showing the relevancy to the users.
B. Hacks: Don’t fall for short tricks. SEO is a time taking process involving dedicated efforts.
C. Short-term strategy: SEO results don’t normally emerge right away, however, there are exceptions, such as when you fix a significant problem. In general, consider months rather than days.
D. Just installing an SEO plugin: SEO plugins are beneficial tools. However, just because you have one does not guarantee your website is now “SEO-friendly.”
E. Ignoring the audience: The more you know about your target audience (customers, readers, and subscribers), the easier it will be to develop an efficient SEO plan.
SEO blogs to follow:
If you are looking for your go-to read for SEO, here is your list:
A. Search Engine Journal: Search engine Journal (SEJ) provides the most recent SEO news, guidelines, webinars, and how-to’s.
B. Search Engine Land: Provides how-to guides as well as the latest developments in the industry.
C. The Keyword: Google’s blog is the place for all of Google’s news and updates.
D. Backlinko: Brian Dean simplifies complex issues into concrete steps, allowing anyone to learn SEO and apply it to their website.
E. SEMRUSH: The Semrush blog also keeps you up to date on the newest news, industry trends, and SEO, PPC, and SEM strategy techniques.
How to learn SEO on your own?
The answer is, Yes, Absolutely.
There are many free and low-cost SEO online courses available. Most are comprehensive, written by specialists, and end with recognition or certification:
A. Google Analytics Academy.
B. HubSpot Academy.
C. Yoast Online SEO training.
D. Semrush Academy.
Last but not least- What is the role of SEO in marketing?
The primary goal of SEO is to increase a website’s visibility in search engines. As such, it is an essential component of any digital marketing plan.
SEO works well with PPC advertising and overlaps with other marketing disciplines such as content marketing and social media marketing.
Looking for some help? Connect with our experts here or simply leave a comment & we will reach out to you.
