WordPress is undoubtedly one of the best content management systems for Search Engine Optimization, aka SEO.
Even though the platform covers a lot, your website would still require some tweaks to handle the nitty gritty of the SEO.
The following article ingrains and outlines all the aspects of SEO to help you improve your ranking, gain more traffic & subscribers, hike your sales & finally build a better website.
Start with the Basics:
With tons of features available to users, WordPress is a well-optimized (CMS) content management system in itself. A simple setup can offer a solid base without considerable modification, theme optimization, and plugins.
Beginners can get going for SEO with WP. Nevertheless, you can do a few things with SEO to improve your workflow, boost your chances of ranking, and guarantee that your website is fully optimized for different search engines.
Following are a few basic steps to ensure a strong foundation to build upon:
1. Your site’s health.
i. Hosting service –
Numerous SEO-related factors are impacted by your hosting,
particularly site speed, uptime, and security.
So how do you choose a hosting service provider? A few things to consider while opting for a hosting provider are-
A. High uptime: Even the most outstanding hosting companies experience downtime. However, if your website goes down too frequently, it damages your reputation and revenue. So keep checking the uptime for your website.
B. WordPress compatibility: The hosting service should work with WordPress websites. Most reputable providers have a package designed specifically with WordPress requirements.
C. Free SSL: A free SSL certificate is a requirement for hosting because it permits your website’s safe HTTPS encryption.
D. Location of a server: For instance, if your primary market is Americans, you’ll want the server to be there so that Americans can access your website more quickly.
E. Good support: Support that is responsive and helpful makes everything simpler.
Connect with us for hosting your website.
ii. Upgrade the PHP –
Although the numbers rapidly declining, many WordPress
websites continue to use the old versions of PHP. WordPress statistics show that some
Website owners continue to use PHP versions from the five series even though PHP 8.0 and higher have been available for years.
These older PHP versions don’t provide any further security fixes and are consequently more vulnerable to attacks. Luckily, the WordPress team has dropped support for anything older than PHP 5.6.20. Currently, the project advises using PHP 7.4 or above to operate WordPress smoothly.
So, updating your hosting environment to a newer version of PHP is one of the most crucial things you can do to improve the performance and security of your site—and, subsequently, your WordPress SEO.
The advantages are as follows:
A. Offers incredible speed.
B. Runs more efficiently.
C. Works well with the new development.
D. Safe & secure.
E. Updated & future-proof.
How much do you know about WordPress? Check here.
iii. Use SSL and HTTPS –
In the past, implementing SSL—obtaining an HTTPS URL and a green padlock icon in the browser URL bar—was optional. It is now necessary to have a working SSL certificate installed, as search engines may “penalize” sites without them (and/or display warnings next to their search results).
Google has acknowledged HTTPS as a ranking factor. Additionally, using SSL on all websites is generally a good idea to stop hackers and other outside parties from intercepting requests and data.
2. An SEO-friendly theme.
The platform’s default “Twenty Twenty-Something” theme will almost probably be visible when you initially install WordPress. However, you could look into several themes if you want to customize your site.
Additionally, you should ensure that the theme you select loads quickly and is light. Website performance is crucial vital when it comes to SEO.
Thousands of free themes are available in the official WordPress theme library (as well as many more premium ones).

You can connect with agencies to get to know the best themes or test a theme yourself:
1. Simply locate the theme demo site (It can usually be found on its official website.)
2. Run the tool after pasting the URL into Google PageSpeed Insights.
You’ve found a simple theme if the Performance results resemble these (i.e., it receives a score of 90 or higher).

3. Make your site indexable.
Your website should be indexable for Google to show it on the search results.
You should review your site’s visibility settings under Settings > Reading.
Here, immediately next to the “Search engine visibility” area at the bottom of the page, is a checkbox:
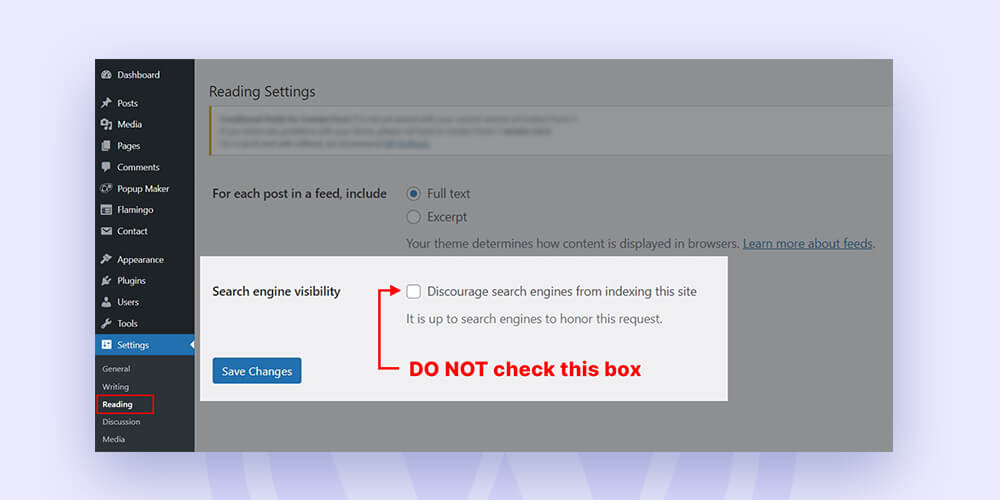
By default, the box shouldn’t be checked. However, developers frequently use it to prevent search engines from crawling a website while it is still being built.
The box should be unchecked if your website is operational and prepared to appear in Google search results.
4. Check the Permalink structure.
If you’re building a new site, you should alter your permalink settings, which can be found under Settings Permalinks. Your permalink settings decide what format your page and post URLs will take, which can greatly impact the SEO.
All your posts and pages will have URLs that resemble example.com/ if your default settings are not changed. Although this is perfectly acceptable, still it could affect how users and search engines view the value and relevance of your pages.
The URLs, elements, ordering, and structure of your website are all changed by changing the permalink structure. Therefore, choosing the proper format while building your website is crucial because changing it later can negatively affect the site’s SEO.
Depending on how much emphasis they intend to place on classifying their material, we typically advise customers to choose a structure that generates URLs that look like – example.com/post-name/ or example.com/category/post-name/.
Both of these selections are ideal for the majority of WordPress sites.
You can choose “Custom Structure” and alter the value to /%category%/%postname%/ to include the category.
What to do If you had done it previously?
When you use p=postid> as your permalink, WordPress will handle all the redirects on your behalf. Additionally, the same applies if you switch from /%postname%/ to /%category%/%postname%/.
5. WWW or non-WWW/ Choose your site’s address format.
It would be beneficial to consider what you wanted your website to display as either www.example.com or just example.com.
Ensure that the version you want to display is accurately reflected in the Settings General section:
There isn’t much of a difference from an SEO standpoint either way. In addition, most hosting and server configurations will automatically route requests to the version you have chosen.
Here are some observations on the subject.
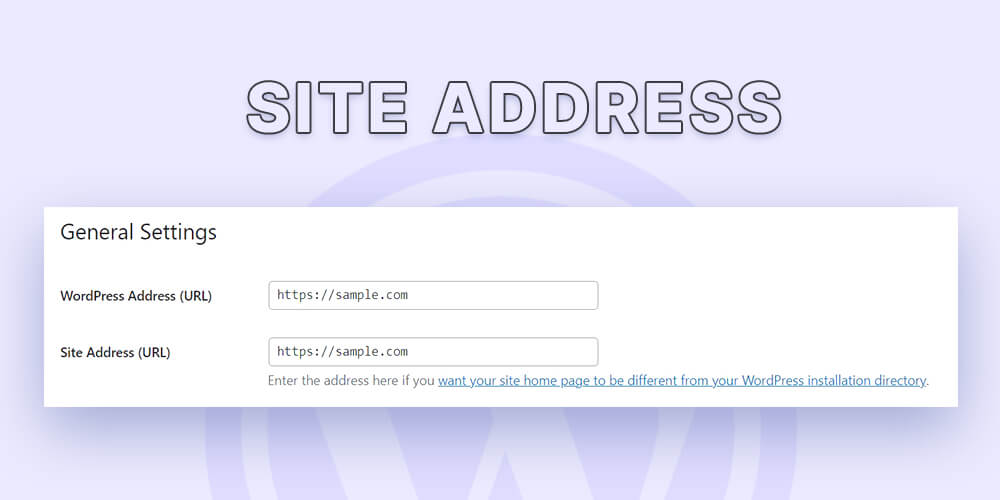
Both the www and non-www variants are treated as separate URLs by Google. To avoid problems with duplicating content, you must choose one.
Neither format significantly affects SEO (as long as you stick to only one version).
In the past, www was present in every URL. Many websites today remove it. But ultimately, it depends on your preferences.
6. Install & configure an SEO plugin.
You may find it simpler to install some fundamental SEO settings and stick to recommended practices if you use a WordPress SEO plugin.
The following are the top three free WordPress SEO plugins for you to consider:
a. All in one SEO.
b. Yoast SEO.
c. Rank Math.
7. Optimize-
1. Content!
The most important factor for SEO is the content that you provide in your niche. People generally search for engaging and authoritative articles to their questions.
Writing and publishing high-quality content for your website that sets you apart from competitors should be your vision. It also means presenting ideas in a well-structured and smooth accessible manner- that is easy to read and understand.
2. WordPress Pages vs. Post.
WordPress by default includes two basic forms of content: posts and pages.
For static pages without a category and maybe without an author, use the Pages format. An “About” page, a “Privacy Policy” page, or landing pages are common examples.
The post format is used for Blog Posts. These pages display the author’s name and the date they were published and are categorized.
The posts on the website are displayed in reverse chronological order (the most recent posts are at the top).
In WordPress, you may decide whether your homepage will be a static page or an index of your most recent content. Just select one of the two choices under Settings > Reading:
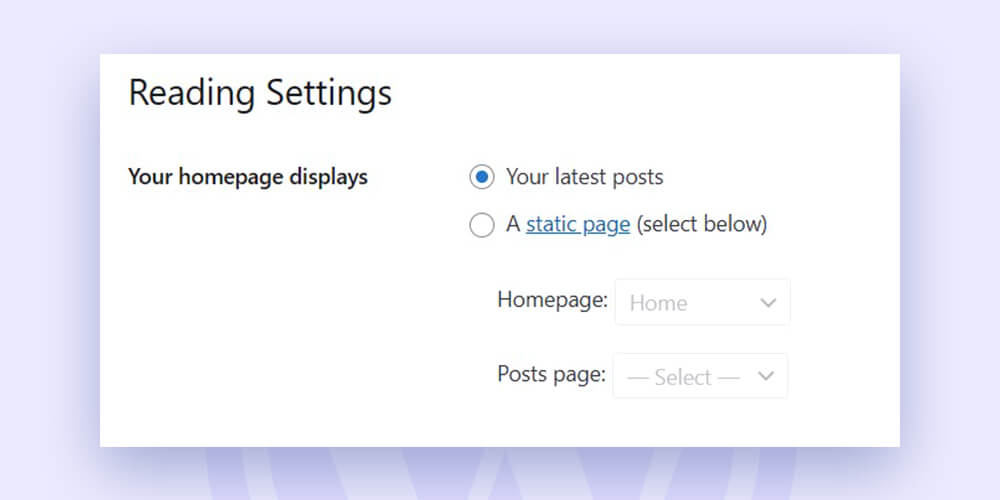
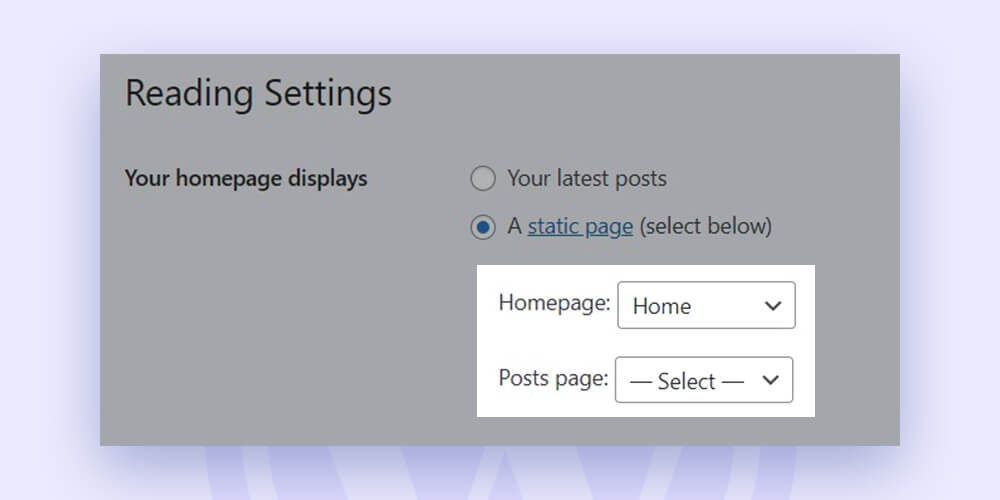
You can choose the page that will serve as your homepage if you choose the static homepage option.
3. Keyword cannibalization.
A site map provides another advantage as well. It assists you in preventing keyword cannibalization, a problem when your pages compete with one another for Google results.
As Google’s John Mueller said in a Reddit AMA:
“If you have several pages with essentially the same material, they will compete with one another… Personally, I prefer fewer, stronger pages than many, lesser ones. Don’t dilute the value of your website.”
So, how can you prevent your pages from clashing with one another then?
This is how:
Every page of your website should have a target keyword assigned.
Ensure that the target term on each page is different as well.
Submit site map for Google Console –
A simple file called an XML sitemap contains a list of all your pages in a language that search engine crawlers can understand. It aids search engines in finding your fresh pages. Additionally, it supplies crucial details (such as when the page was last updated).
WordPress automatically generates a sitemap. You’ll find it at the following URL: https://www.yoursite.com/wp-sitemap.xml
However, Yoast SEO will produce a little more sophisticated XML sitemap and disable the default one if you’re using it. Simply entering the sitemap URL into Google Search Console will do the job for you.
Nest your website’s pages –
When you “nest” your pages, you organize related pages into separate directories within your URL structure. WordPress generates URLs without nesting by default.
For instance, without nesting, the URLs on a website for a freelance photographer would resemble this:
– domain.com
– domain.com/services
– domain.com/wedding-photography
– domain.com/portrait-photography
– domain.com/family-photography
– domain.com/blog
– domain.com/editing-process
– domain.com/family-portrait-tips
However, we might nest the pages in the following manner to make the URL structure more logical—(don’t forget that search engine crawlers favor order and structure)
– domain.com
– domain.com/services
– domain.com/services/wedding-photography
– domain.com/services/portrait-photography
– domain.com/services/family-photography
– domain.com/blog
– domain.com/blog/editing-process
– domain.com/blog/family-portrait-tips
The pages in the above example are layered into more detailed categories. The blog postings are contained in the “Blog” directory, while the services offered are nested in the “Services” subfolder.
You must update the page to nest it in WordPress. Then, pick the desired “Parent Page” under “Page Attributes.”
As an illustration, you might choose “Services” as the parent page for the wedding photography page.
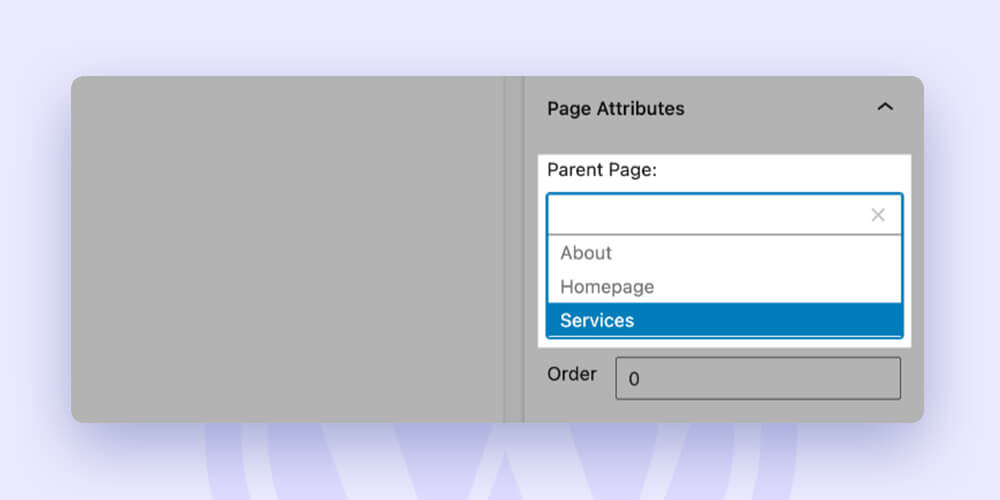
That would result in the URL for the wedding photography page being changed to domain.com/services/wedding-photography.
So go ahead make a structure and nest your pages.
Easy to navigate the menu –
Your website’s MENU should be straight, simple, and easy to navigate. Additionally, SEO benefits from it. because it provides more detail on the layout of your website and its important pages.
The menu should be:
A. Clear- Stay away from creating too many menus. If required, create and add a submenu and move less used URLs in the footer.
B. Simple & Helpful- Stick to the “User First” mantra. Put yourself in the user’s shoes and make sure that the navigation is crystal clear.
C. Predictable: Don’t try anything new. Use standard titles (such as “Pricing” instead of “How much will it cost” or “Blog” instead of “Field notes”) and include items that people (and search engine crawlers) would expect to find on a menu.
Here are a few instructions to help you out:
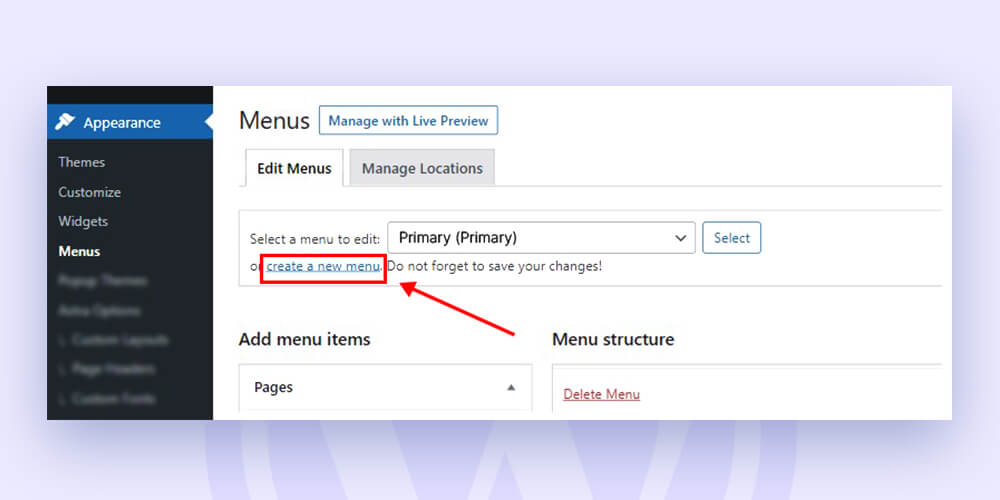
1. Click the “Create a new menu” link or go to Appearance > Menus and edit your menu there.
2. The “Add menu items” portion of your menu lets you add pages (or other kinds of content) to it.
3. In the “Menu structure” area, you can drag and drop the menu items to reorder or rename them.
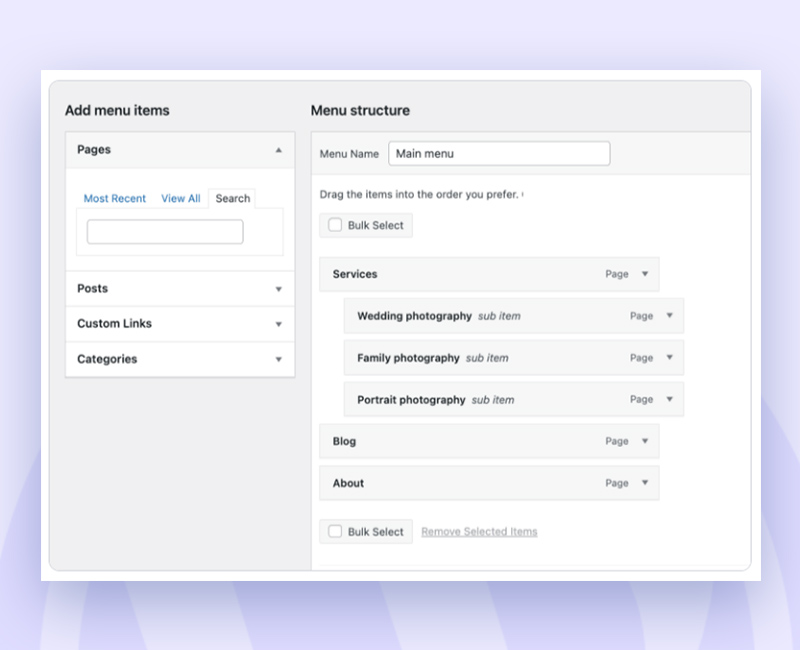
Don’t forget to mark the menu as “Primary Menu” in the settings at the bottom if you want it to appear in the website’s header:
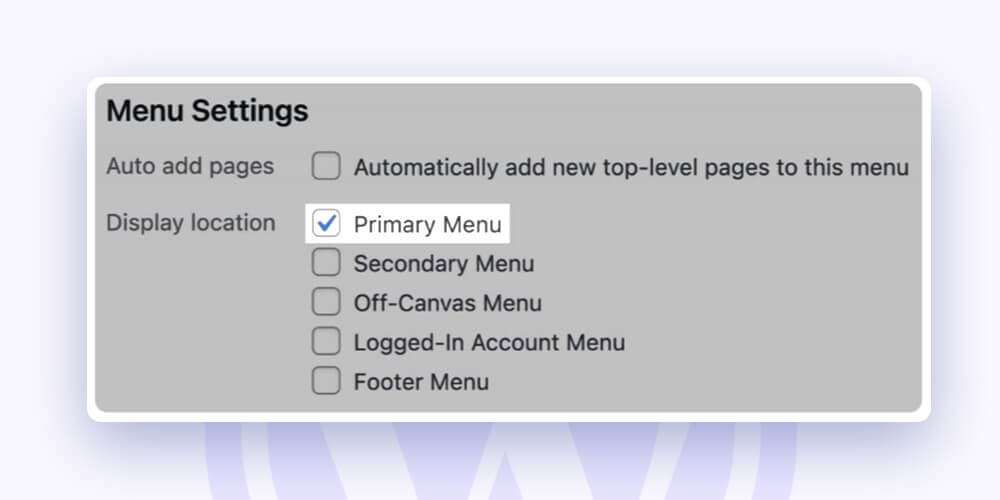
In WordPress’ “Menus” section, several menus can be created (e.g., a footer menu, standalone blog navigation, etc.). Your theme and/or page builder will determine how they are implemented.
Create a post category –
Using categories can help you with:
Group your blog logically: Since categories can be nested, they offer a special chance to establish a hierarchy within your blog themes.
Internal links: Your category archive pages can serve as helpful content hubs, interlinking all the pertinent pieces covering a single topic, and enhancing the internal linking of your website.
Categories: Organize your posts into categories to make it easier for readers to find additional topics that are connected to them.
Since categories are required for WordPress posts (WordPress will use the default “Uncategorized” category if you don’t specify one), you might as well make the most of them.
It’s simple to give your post a category. Open the page’s editor, then navigate to the right panel to find the Categories area.
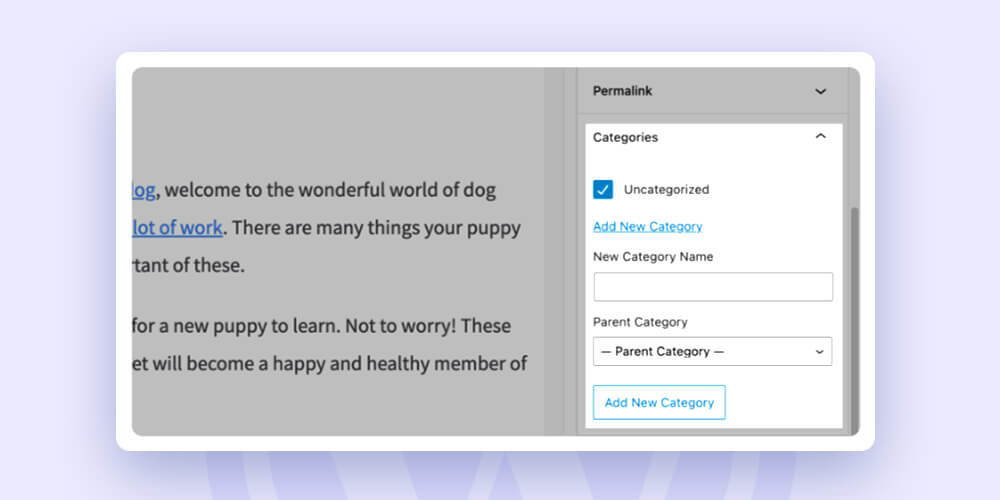
Optimize the categories with-
1. The number of categories –
The number of categories you can utilize is not constrained in any way. However, the recommended range for categories on your site is between five and ten to make it simple to navigate without overloading the viewer.
Here is an example of the WordPress.org menu for you:
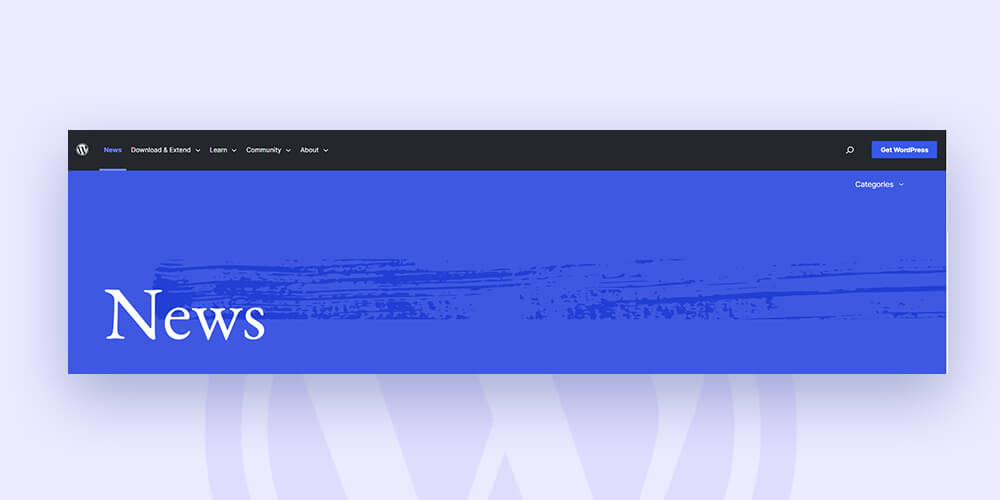
The main menu has 5 categories which are further divided into subcategories as follows:
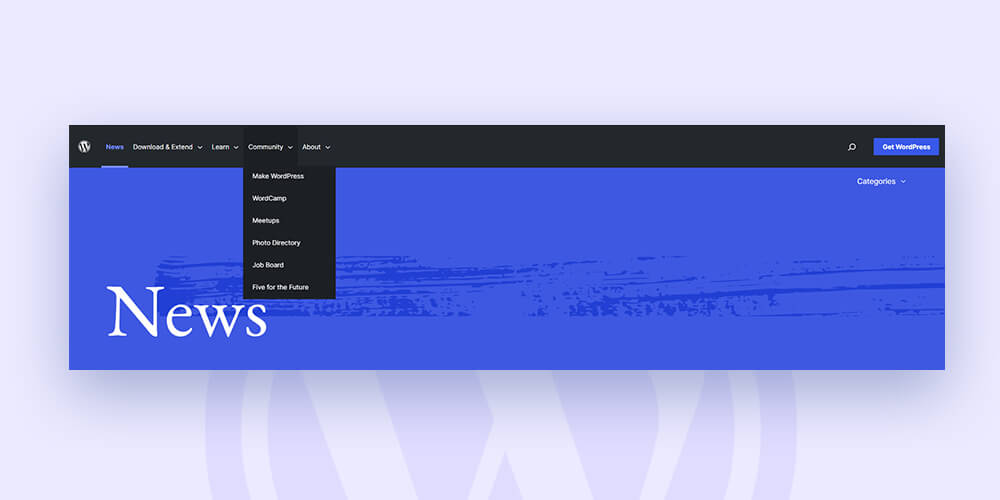
Try to categorize things broadly. In this manner, you avoid having categories with few posts in them.
2. Optimize the category pages –
A concise description should be included on each category archive page. By doing so, you may introduce readers to the category while also giving search engines original information.
As we previously said, category archive pages may help you build fantastic content hubs by acting as “subject gateways” for various blog posts.
They should be indexed and show up in the SERPs because of this (search engine results pages).
You should optimize the title tags and meta descriptions of your category pages to create attractive search result snippets.
3. Breadcrumbs –
The primary benefit of using breadcrumbs is that they make browsing easier for website users.
Second, they might appear in search results, improving your SERP snippets.
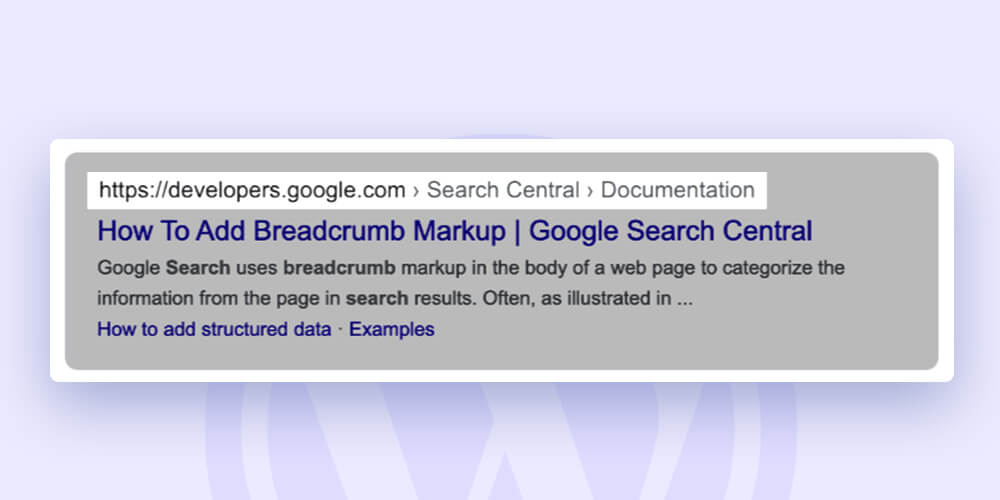
Using Yoast SEO is the simplest approach to enable breadcrumbs on WordPress. Click “Breadcrumbs” under “Search Appearance” and then “Enabled” on the following page.
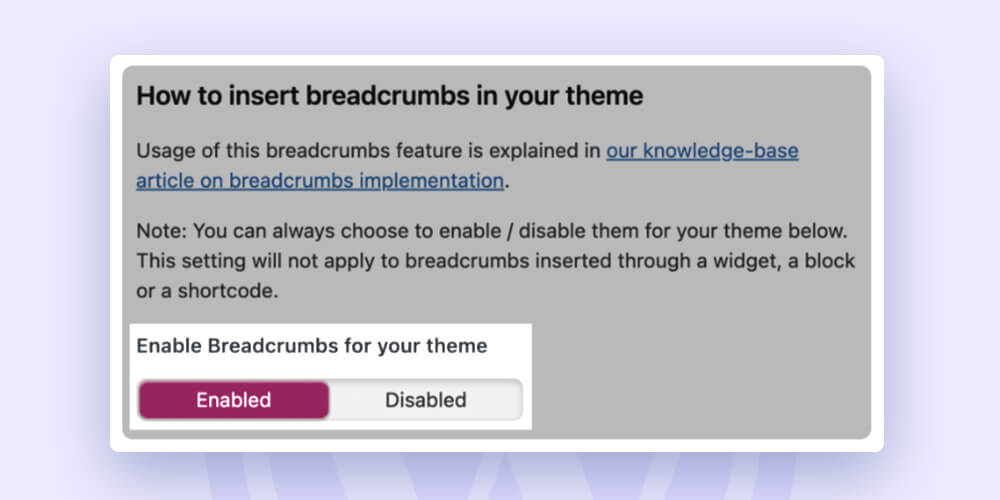
Keyword research –
To target your ideal audience and rank on Google to get traffic, among many other steps number one is to find the keywords.
To make things easier for you here is the process of keyword research explained:
1. Find the right keywords –
Step one is to look at what your competitor ranks for. The ‘Keyword Gap’ analysis is a way to identify those keywords that your competitors rank high for, and you don’t.
An excellent tool to carry out this process is SEMRUSH. You only need to enter your domain and up to four of your rivals’ domains. (You can manually enter some, or the tool will recommend some.)
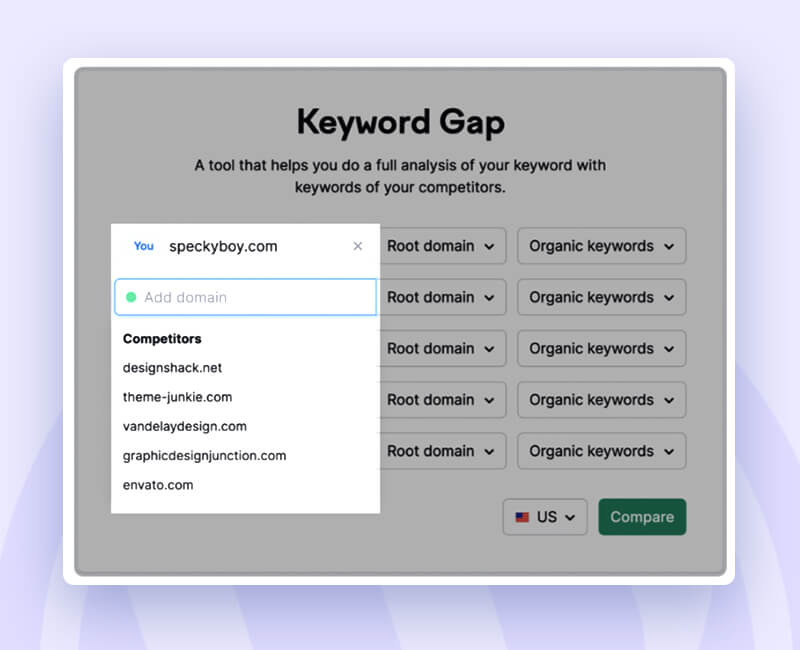
Hit the compare button.
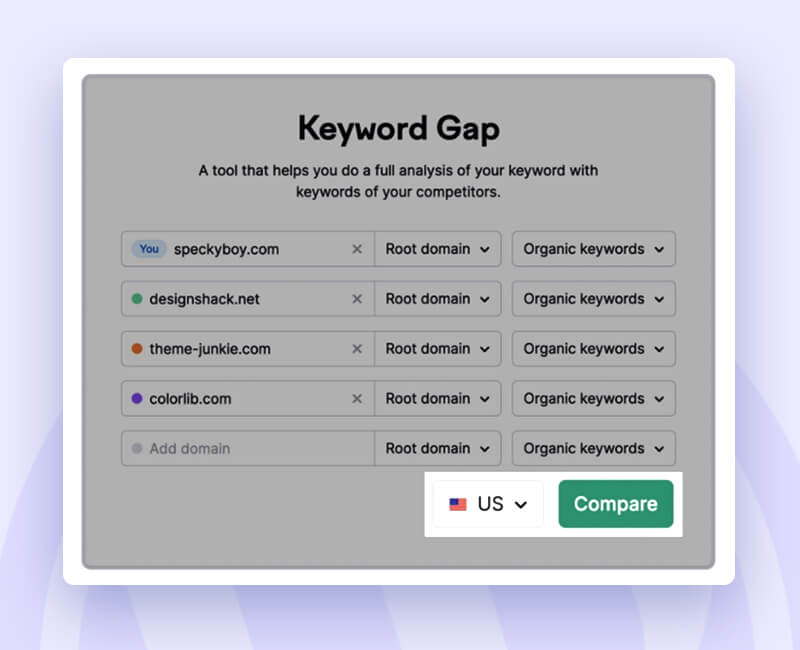
Follow the tabs to find:
Missing: The keywords your competitors focus on and you don’t.
Weak: The keywords on which your competitors rank higher than you.
Check out the list and get your inspiration.
Choose the right keywords –
After discovering the keywords, you must carefully examine their metrics to select the target keywords—keywords that will accurately describe each of your sites or posts.
You must examine metrics closely before selecting target keywords. Namely:
1. Search Volume: How often people look for a particular keyword.
2. Keyword Difficulty, aka KD: How difficult (in %) is it to rank on a keyword?
3. Search Intent: The kind of content expect from a keyword.
Optimize the content for the target keyword after determining your ideal page or post’s target keyword.
That doesn’t mean you overuse the keywords or stuff them in your content.
Instead, incorporate the target term (or its variations) into a few of the page’s most important parts, like:
– Headers
– Title tag
– Body
– Internal links.
Well… create amazing content –
So, what should you keep in mind while creating content?
One word- search intent. Start with analyzing the SERP of the targeted keywords.
Just scan the results and focus on the first few pages. You may accurately determine search intent using the SERP analysis by:
A. The right kind of content- You may target the keywords with the appropriate type of content by seeing what kinds of content (such as landing pages, reviews, informational posts, etc.) are ranked for.
B. Understand the topic- Find the questions the readers are looking for and answer them in your articles.
C. Research your competitors- See which pages of your competitors are ranking.
D. Provide additional value- Observing what your competitors have written can help you think of ways to differentiate yourself from them (by providing a unique angle, data, examples, media, etc.)
1. Follow EAT guidelines.
One key concept that Google favors for SEO is – E.A.T – Expertise, Authoritativeness, and
Trustworthiness. Having high-quality backlinks is related to showing good E-A-T in a big way. However, numerous on-page best practices will also assist you in that area. Namely:
Writing on subjects related to your area of expertise.
Providing details about your authors’ backgrounds and areas of expertise.
Being thorough and accurate about the facts.
Supporting your claims with statistics and other trustworthy data.
Transparency in your website’s description (About page, Contact page).
2. Optimize the content for readers.
Most of the time, the focus is generally on ranking. With ranking being the focus, the users or readers are left out.
While preparing your content, keep your ‘User’ high priority with the ranking. This way, you can satisfy your readers while raising the SEO.
SEO-friendly URLs.
Long URLs are problematic since search results usually truncate them, like the following:
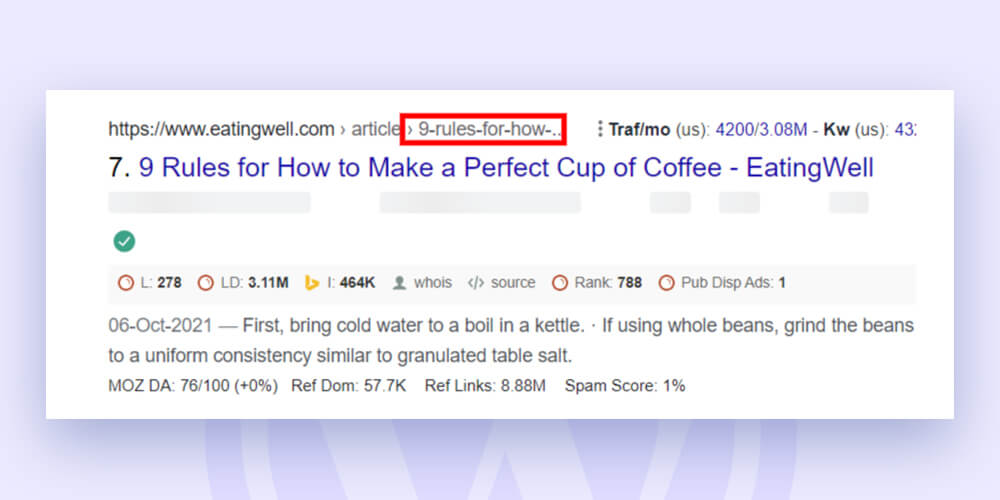
Change the “URL Slug” in the “Permalink” section of the page/post editor to make a URL that is more SEO-friendly. Alternatively, you can modify URLs under the Yoast SEO settings at the editor’s bottom.
Here are some other pointers for making SEO-friendly URLs:
Keep it brief: It will not be truncated in search results, and it looks better.
Include the targeted keywords: This facilitates people to understand the page’s content quickly and serves as a ranking factor.
Include no numbers unless you are certain they won’t change: You would have a URL that is inconsistent with your content if the number in the post changed in the future (for example, the number of tips or the year).
Use headers –
Some of the most crucial components in the layout of a single page are the headers as:
a. They establish the page’s content structure.
b. They clarify the page’s content and break up the text to make it easier to read.
Open the page or post in the WordPress Gutenberg editor to add headings. Then, click the Plus (+) icon to add a new block. Choosing “Heading”:
Then, select what type of heading you need:
You can access your document outline to check how your page is set up by headings. Simply select “Info” from the editor’s top navigation. Look for the word ‘i’ is enclosed in a circle.
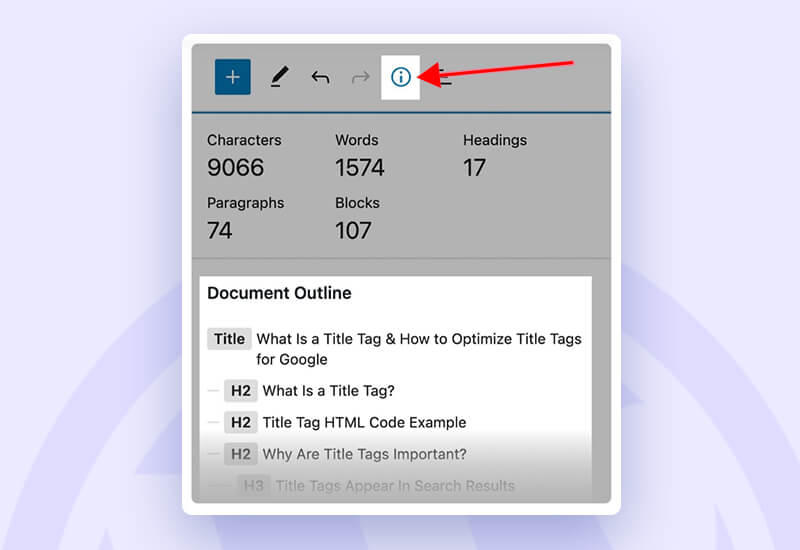
Next, you can analyze the following issues:
a. Are the headings logically nested? H3s below H2s, etc.
b. Are headings on the same level grammatically and stylistically consistent?
c. Could a table of contents made up only of the titles still make sense?
If you answered “yes” to each of these inquiries, congratulations! Your headings are on point.
Optimized title tags –
The title tag of your website describes the content of your page to both people and search engines. Additionally, it’s a key ranking component.
It appears in browser tabs and search engine snippets as follows:
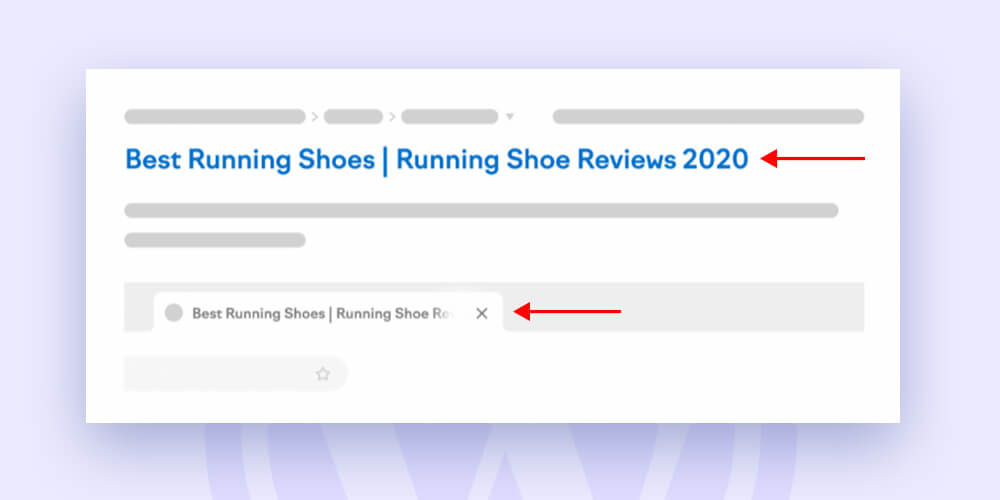
Therefore, creating powerful, SEO-friendly title tags is a crucial on-page SEO task.
Here too, the Yoast SEO plugin can be useful. Simply modify the field under “SEO title” at the bottom of the page you are editing:
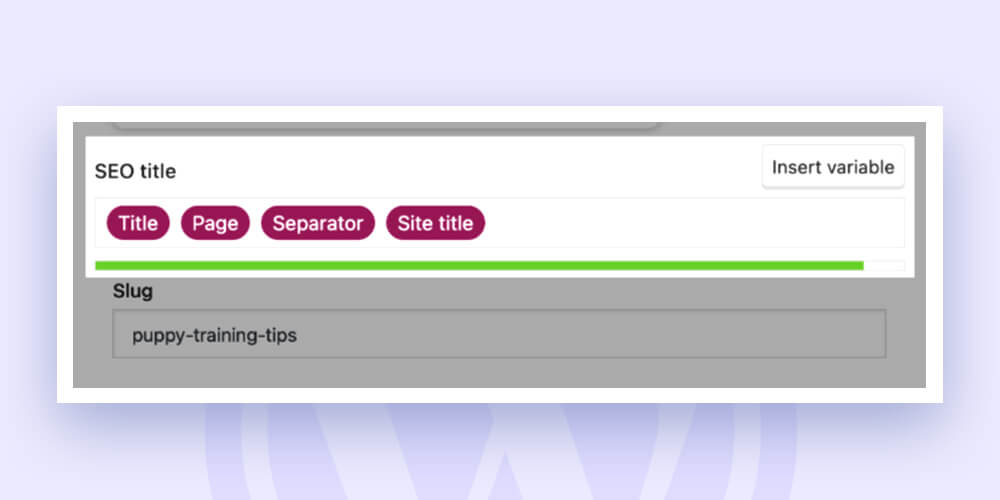
The post or page title will be automatically entered into the “Title” and “Page” placeholders.
You can eliminate them and create a unique, SEO-friendly title tag instead. Sometimes, you have to condense the title and make a few word changes.
Here are some guidelines for creating captivating title tags:
- Create distinct titles for each page and post.
- Make sure the title tag is no wider than 600 pixels (you can check this using the progress bar located beneath the “SEO title” form in the Yoast SEO plugin; aim to stay in the green zone).
- Prioritize your goal keyword (but avoid stuffing the page with keywords).
- If you can, mention your brand (sometimes it can make the title too long, so this depends on your needs).
- Use convincing, actionable language (such as “review,” “best,” “checklist,” or “step-by-step”).
- Use numbers (phrases like “top 10” or “in 2022” are attention-grabbing).
Craft meta description –
Although they don’t directly affect rankings, meta descriptions affect your CTR (click-through rate).
In other words, creating engaging meta descriptions can increase the number of times searchers click on your link. Yoast SEO allows you to add meta descriptions in the same section as title tags. You can stay inside the recommended length range for your meta description by using the progress meter.
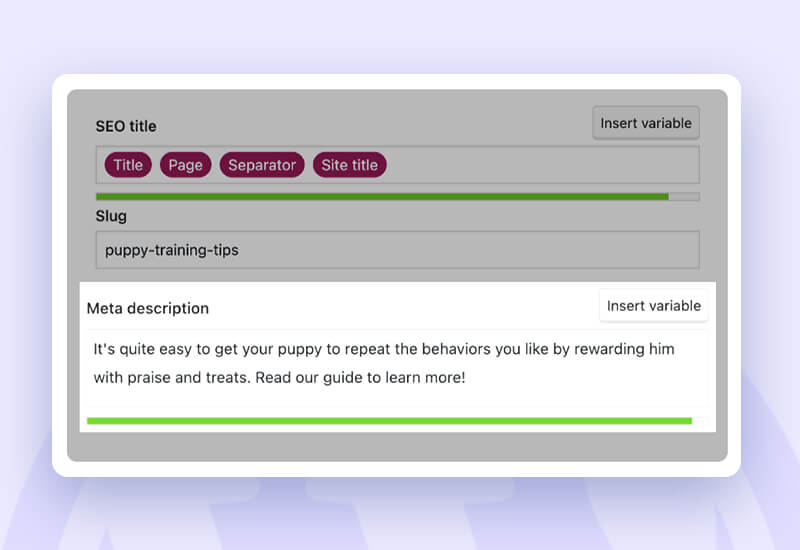
The guidelines below will assist you in creating fantastic meta descriptions:
- Give each page a distinct meta description.
- Aim for 120 characters (to avoid being cut off in mobile results).
- Add your intended keyword here (again, do it naturally, without keyword stuffing)
- Keep the search intention in mind
- Use a clear, active voice.
- In the end, add a call to action and demonstrate value.
Internal linkage –
Any link that leads from one page to another on the same domain is considered an internal link.
There are two types of internal links:
A. Navigational Links: These links make the website’s navigational structure, such as menus, categories, or breadcrumbs.
B. Contextual Links: These internal links inserted within the body copy point to pertinent pages on your website.
Internal links are a good approach to transferring authority from one website to another in a way that is completely in your control (unlike backlink development).
Before posting, make sure to link to posts or pages that can be helpful to your audience in your new piece of content. Once the post has been published, search for any earlier posts that might connect to the new content.
Image alt Text –
It’s crucial to use descriptive alt text when uploading photographs/pictures to WordPress or other comparable platforms.
According to the Google Search Central blog, Google employs alt text to “understand the subject of the image”.
For WordPress, here’s how to add alt text to an image:
- You can choose the image you wish to alter by going to Media > Library. In the “Alt Text” section, enter your alt text.
- Keep in mind that alt text is not always required. There is no requirement for alt text for:
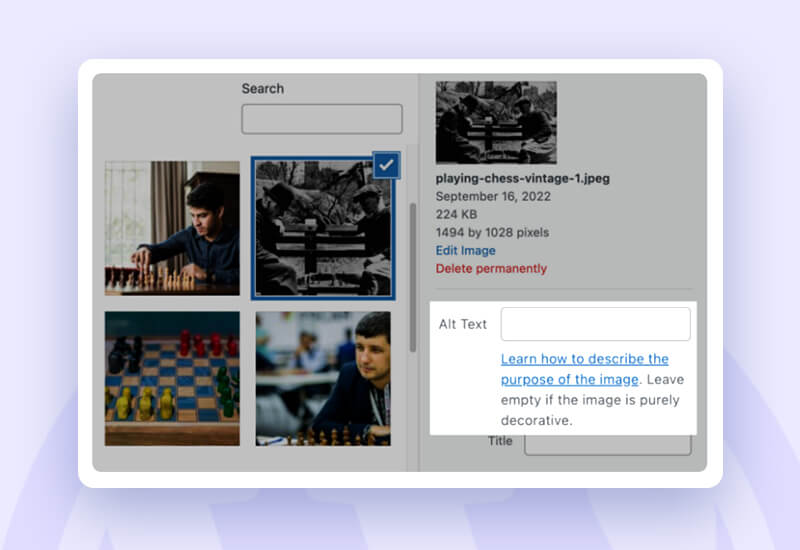
Images with only a decorative intent
Adjacent images with content that is likewise written in real text.
Site’s speed optimization.
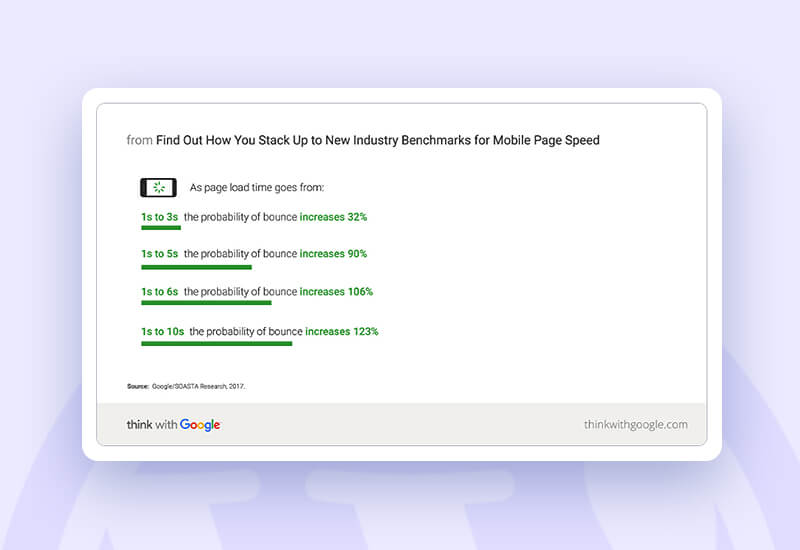
Every second matters when it comes to page speed or the website’s loading speed. It is another established ranking factor is page speed. Therefore, having a slow website can harm your search engine results.
Additionally, a Google study found a direct link between longer page loads and the likelihood that a user may leave the website:
Your WordPress website can be optimized in a variety of ways to increase page speed:
- Installing a caching plugin will enable faster response times for subsequent requests by storing some website data after the initial load.
- Making use of a Content Delivery Network The content of your website is distributed globally by CDNs to speed up loading times in places farther from your original server (An example of a popular CDN service is Cloudflare.)
- Making your code smaller: Your source code may load more quickly if you make it smaller (for example, by eliminating extra characters).
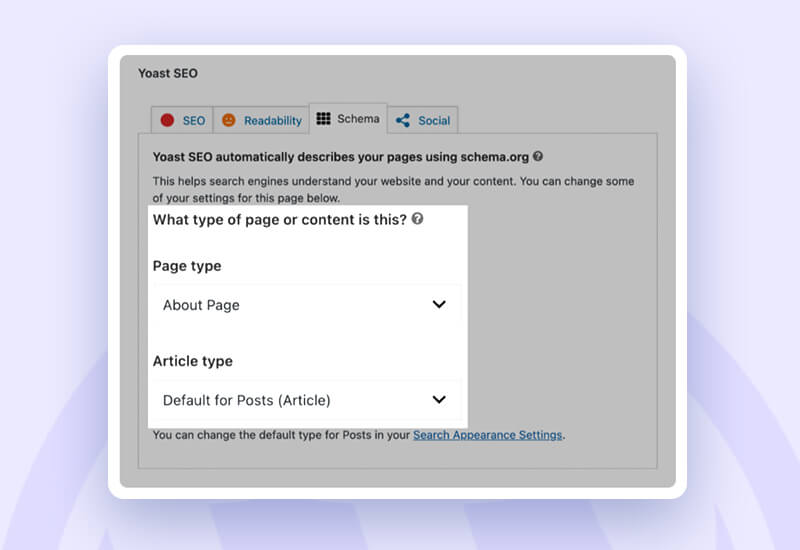
Schema Markup.
A piece of code known as structured data, which is written in a certain format known as schema markup, aids Google in comprehending the content of a page.
Let’s take the example of a recipe blog that provides thorough, step-by-step instructions for every dish.
You may make it easier for Google to read and comprehend these individual steps by adding the HowTo markup, which allows you to mark up each step as well as how long the task will take.
Moreover, the default WordPress (Gutenberg) editor allows you to add a few Yoast structured data pieces. To add a new block, simply click the Plus (+) icon and type “Yoast.” You can include a FAQ block and a how-to block.
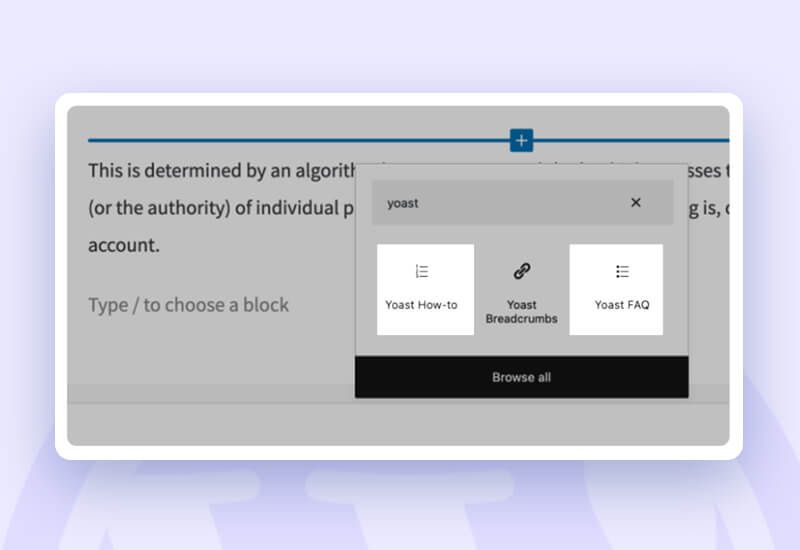
You may add specialized structured data that Yoast does not support. Use one of the many schema markup-specific WordPress plugins.
Secure your website.
SEO includes website security as a core component (although it may not be obvious initially). The research found that manipulating a site’s outgoing connections is one of the most frequent causes of hacking (i.e., to make your site link to another site without you knowing about it). Linking to spammy, unrelated websites will definably harm your search engine rankings.
Here are a few steps that you can take to ensure the security of your website:
A. Use a Backup plugin.
B. Use a security plugin.
C. Update regularly.
D. Install only verified & trusted plugins.
Promote your website.
Thanks to WordPress SEO, you put a lot of time and attention into your website’s content and ensure readers can find it via search engines. But there are additional strategies you may use to get readers to your WordPress blog.
But how can you attract and expand such a following? It won’t work only to create and publish posts; you also need to advertise and promote your website!
1. Work on engagement:
Interacting with readers is always enjoyable, but how can you get them interested?
Refer to all the different methods & strategies to make your readers engage with the piece. It could involve making a comment, engaging it via social media, or engaging with the subject directly via email marketing.
But how do you engage people? Always feel free to ask them! Engaging writing should be followed with a question to your audience. To continue the dialogue and create relationships with your readers, reply to these comments.
2. Grow your reach:
Social networking is the best strategy to expand and reach your blog’s audience. You should be active on all those social media platforms where your (possible) audience generally interacts. Several well-known social media platforms include Twitter, Facebook, Instagram, and Pinterest.
3. Email marketing:
It’s frequently a good idea to invest in a newsletter and use social media to promote your site. Allow folks to subscribe so you can send emails with your newest blog entries and other interesting information.
Ensure to provide a subscription area underneath your content and in other prominent locations on your website. Make sure your newsletter is responsive to mobile devices. But most importantly, make sure your newsletter is unique!
4. Amplify your content:
Because so many blogs are written daily, it’s challenging to stand out. There’s a good probability that your articles may get lost in the deluge of content. You must magnify your content if you want it to live up to its full potential.
Your chances of reaching new audiences increase if your content is unique and well-organized. Examine your options for acquiring new viewers outside of your organic audience.
Running ads on Facebook or Instagram could be a fantastic method to expose your content to new audiences.
Simply analyze the channels you now employ and identify where you may increase your efforts to reach a wider audience.
The most common FAQs.
1. Is WordPress good for SEO?
WordPress does indeed support SEO well. But all it is is a CMS. So, if you want your website to rank well in organic search, you’ll still need to put in the effort.
2. Does Google favors WordPress sites?
Google favors no CMS. WordPress may be more SEO-friendly than other CMSs, but in most cases, SEO success is not determined by the CMS used. Having said that, WordPress is unquestionably a wise SEO decision.
3. Which is the best SEO plugin for WordPress websites?
Three of the most well-liked all-in-one SEO plugins are Yoast SEO, All-in-One SEO, and Rank Math. Naturally, there is a tonne of additional excellent WordPress SEO plugins devoted to particular SEO tasks.
You can perform a lot of things with WordPress SEO for your website after reading this article. It covers various topics, including conversion, content, discussion, and technical SEO suggestions. But there’s a catch: you’ll need to put in a lot of effort and produce excellent content if you want to rank for highly competitive terms.
Stay ahead of the competition, and subscribe to our newsletter for the latest updates!
